Hey there, electronics enthusiasts! Welcome to my blog, where we dive into the fascinating world of circuits and components.
Today, I’m super excited to talk about diodes—those tiny but mighty devices that power everything from your phone charger to solar panels. Whether you’re a student, a hobbyist, or just curious about how electronics work, this guide is for you.
What is a Diode?
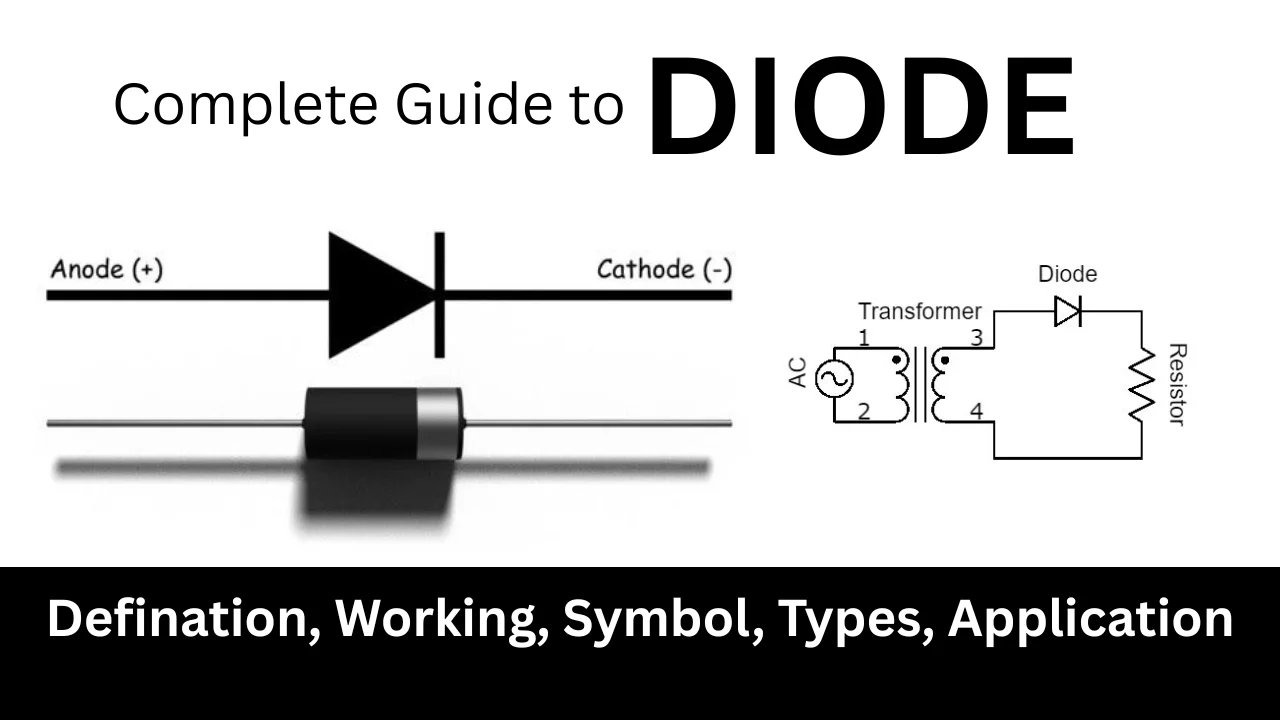
A diode is a semiconductor device that permits current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction, acting as a one-way valve for electrical current. Diodes are essential for rectification, signal modulation, and circuit protection.
From power supplies to communication systems, diodes play a critical role in modern electronics. Diodes are everywhere, your laptop charger, LED lights, and even car electronics rely on them.

Key Characteristics :
-
Unidirectional Flow: Diodes allow current to pass when “forward-biased” (more on that later) but stop it when “reverse-biased.”
-
Made of Semiconductors: Diodes are built using materials like silicon or germanium, which have special electrical properties.
-
P-N Junction: The magic happens at the junction of two types of semiconductors—P-type (positive) and N-type (negative).
How Does a Diode Work?
Let’s dig deeper into how they work? Okay, It’s all about the P-N junction and a bit of electrical wizardry.
The Working Principle
-
Forward Bias: When you connect the positive side of a battery to the diode’s anode (the P-side) and the negative side to the cathode (the N-side), the diode “opens” and lets current flow. For silicon diodes, this happens once the voltage hits about 0.7V—think of it as the diode’s “entry fee.”
-
Reverse Bias: Flip the battery, and the diode says, “Nope!” It blocks the current, acting like an insulator. This is super useful for protecting circuits.
-
Breakdown Voltage: If you push too much voltage in reverse, the diode might give in and conduct (this is normal for some diodes, like Zener diodes, but we’ll get to those).
Real-World Example
Picture a diode in a phone charger. It takes the alternating current (AC) from your wall outlet and converts it to direct current (DC) that your phone needs. That’s called rectification, and diodes are the MVPs of this process
The Diode Symbol: What It Looks Like in Circuits
If you’ve ever seen a circuit diagram, you’ve probably noticed a diode’s symbol. It’s simple but tells you everything you need to know:
-
Standard Diode: A triangle pointing to a vertical line. The triangle’s base is the anode, and the line is the cathode.
—->|—- -
Zener Diode: Similar, but the cathode line has a little “Z” shape.
—->|Z— -
LED: Looks like a diode with arrows showing light coming out.
—->|>—-
These symbols help you figure out how to place a diode in a circuit. Always make sure the anode faces the positive side for current to flow!
A Simple Diode Circuit: Half-Wave Rectifier
Let’s look at a basic circuit to see a diode in action—a half-wave rectifier. This circuit turns AC into pulsating DC, which is a starting point for powering electronics.
Circuit Setup
-
AC Input: An alternating current source (like from a wall outlet).
-
Diode (D1): Connected in series, it lets current pass during the positive half of the AC cycle.
-
Load Resistor (R1): Represents the device you’re powering.
-
Output (Vout): You get a pulsating DC signal.
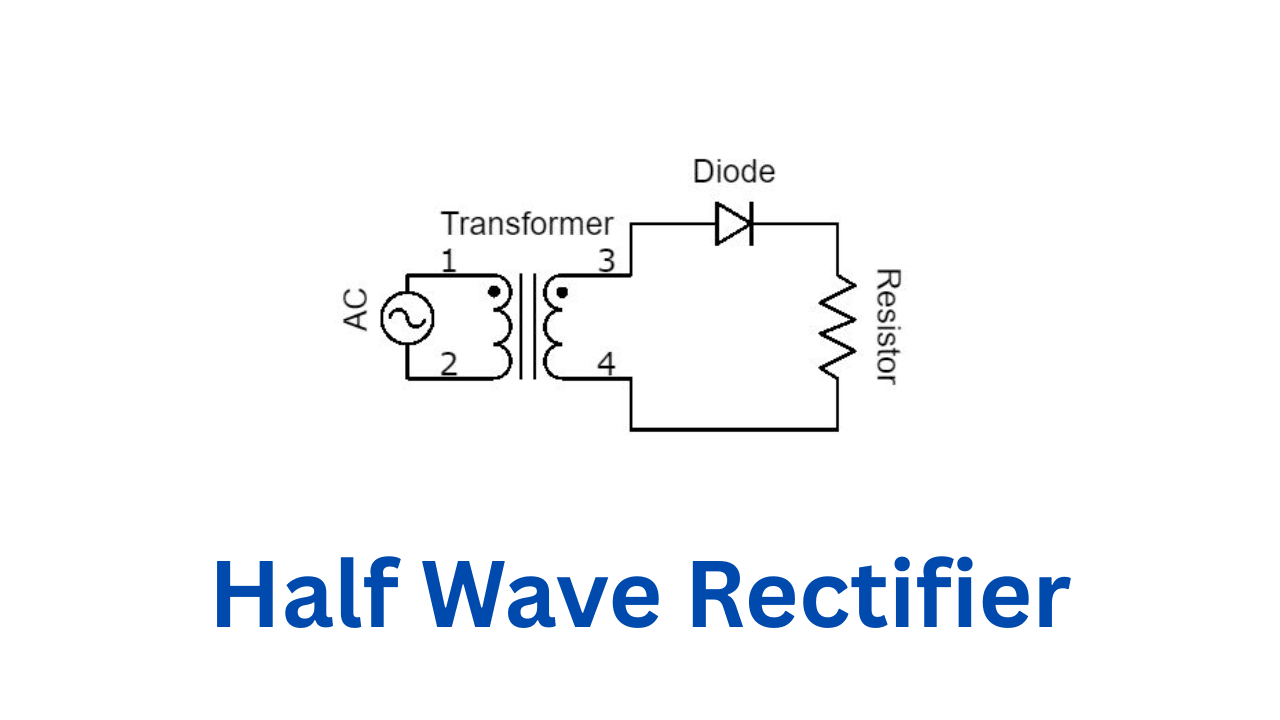
How It Works
When the AC signal is positive, the diode conducts, sending current to the load. When it’s negative, the diode blocks the current. The result? A choppy but usable DC output. For smoother DC, you’d add capacitors, but that’s a story for another post!
Types of Diodes and What They Do
Diodes aren’t one-size-fits-all. There are tons of types, each with a special superpower. Here’s a quick rundown of the most common ones:
|
Type |
What It Does |
Where You’ll Find It |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard Diode |
General-purpose, one-way current flow |
Power supplies, circuit protection |
|
Zener Diode |
Conducts in reverse at a specific voltage |
Voltage regulation, surge protection |
|
Schottky Diode |
Super-fast, low voltage drop |
High-frequency circuits, power converters |
|
LED |
Emits light when current flows |
Lights, displays, indicators |
Fun Fact
Ever wonder why LEDs are so energy-efficient? They convert electricity directly into light, unlike old-school bulbs that waste energy as heat. That’s why your LED TV looks amazing and doesn’t burn a hole in your electricity bill!
Applications of Diodes
Diodes are like the unsung heroes of electronics. You’ll find them in:
-
Power Supplies: Converting AC to DC for your gadgets.
-
Circuit Protection: Saving circuits from reverse polarity or voltage spikes.
-
Lighting: LEDs in everything from streetlights to your smartwatch.
-
Communication Systems: Schottky diodes in 5G networks and radios.
-
Automotive: In car alternators, battery management, and LED headlights.
-
Renewable Energy: Diodes in solar panels and wind turbines for efficient power conversion.
-
Medical Devices: Powering MRI machines and diagnostic tools.
Basically, if it’s electronic, there’s probably a diode involved!
Manufacturing of Diode How Diodes Are Made?
Lets look at the process :
-
Wafer Fabrication: Start with a super-pure silicon wafer (like a blank canvas).
-
Doping: Add tiny amounts of impurities (like boron or phosphorus) to create P-type and N-type regions.
-
P-N Junction: Where the P and N regions meet, you get a diode’s core.
-
Packaging: Encase the diode in plastic or metal (like DO-41 or SMD packages) for protection.
-
Testing: Check if it works perfectly before it hits the market.
we’re becoming a global player in producing Diode
As an Indian electronics enthusiast, I’m thrilled to share that India is stepping up its game in diode manufacturing. Thanks to initiatives like Make in India and the India Semiconductor Mission.
Few Companies India producing Diode, Big names like Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Vishay India, and Diodes Incorporated are leading the charge, alongside small and medium enterprises. You’ll find diode production hubs in cities like Bangalore and Hyderabad.
Why It Matters to produce diode
India’s booming demand for electronics, think 5G, electric vehicles, and solar power, means we need more diodes. Plus, government support is helping local manufacturers compete with giants like China.
Advantages, Limitation and Future of Diode
Advantages
-
Tiny but Mighty: Diodes are small, making them perfect for compact devices like smartphones.
-
Efficient: Low power loss, especially in Schottky diodes.
-
Versatile: From rectification to lighting, they do it all.
-
Affordable: Mass-produced, so they’re budget-friendly.
Limitations
-
Voltage Drop: Silicon diodes lose about 0.7V, which can affect efficiency.
-
Reverse Breakdown: Too much reverse voltage can fry them.
-
Heat Sensitivity: Performance can dip at high temperatures.
-
Current Limits: Not great for super-high currents without extra gear.
The Future of Diodes, What’s Next?
Diodes are evolving to keep up with tech trends. Here’s what’s on the horizon:
-
Wide Bandgap Diodes: Made from materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or gallium nitride (GaN), these handle high power for electric vehicles and renewable energy.
-
Smaller Sizes: Perfect for IoT devices and wearables.
-
Eco-Friendly: Greener manufacturing to save the planet.
-
AI Integration: Diodes in smart systems for better power management.
The future is bright (pun intended) for diodes!
Conclusion
Diodes may be small, but they’re game-changers in electronics. From powering your gadgets to enabling India’s tech revolution, they’re everywhere.
Got a circuit project in mind? Try experimenting with diodes, maybe build a simple rectifier or light up an LED! If you have questions or want more diode tips, drop a comment below or connect with me on social media. Let’s keep the electronics vibe going!
If you liked this article, don’t forget to check back daily!
I regularly post updates on the latest trends in electronics, new product launches, tech innovations, industry news, and updates from electronic companies.
Follow the blog or bookmark this site to stay ahead in the world of electronics!
Feel free to share this article on your favorite social media platforms!