Hey there, tech lovers, students, and DIY electronics buffs! Welcome back to my electronics blog, where we unpack the magic behind the components that power our world.
Today, we’re diving into capacitor those tiny energy-storing champs that keep our devices running smoothly.
Whether you’re an engineer, a curious student, or just seeking out over tech, this guide is your one-stop shop for understanding capacitors
What is a Capacitor?
It’s an electronic component that stores energy in an electric field between two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric.
Capacitors are like the unsung heroes of circuits, managing energy, filtering signals, and keeping things stable.
You’ll find capacitors in everything from your smartphone to industrial machines, making them a cornerstone of modern electronics.
Key Characteristics of capacitor
-
Capacitance: Measured in farads (F), but usually in microfarads (µF) or picofarads (pF). This tells you how much charge a capacitor can hold.
-
Types: From ceramic to electrolytic, there’s a capacitor for every job.
-
Polarity: Some capacitors (like electrolytic) are polarized (they care about direction), while others (like ceramic) are non-polarized.
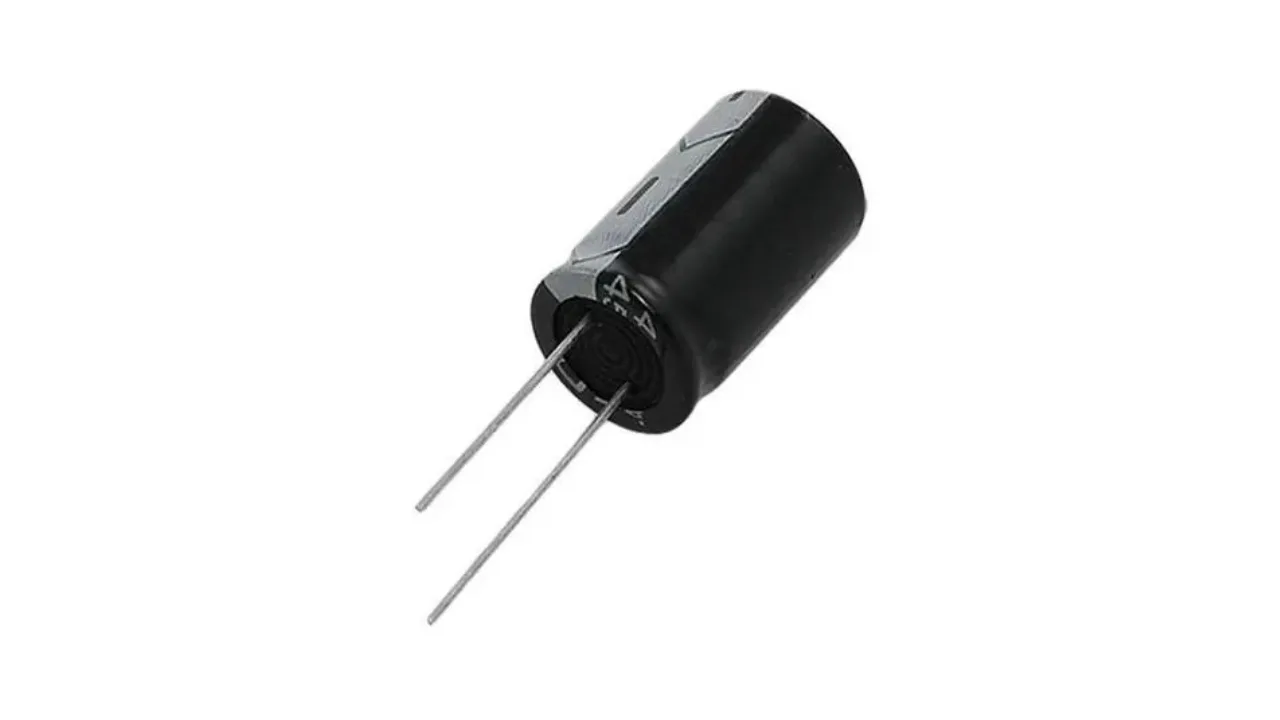

How Does a Capacitor Work?
Let’s break down the magic of capacitors in a way that clicks. They’re all about storing and releasing energy, but how?
The Working Principle of Capacitor
Capacitors store energy by collecting electric charge on their plates when connected to a power source. The dielectric between the plates stops direct current (DC) from flowing but lets alternating current (AC) pass through. This makes capacitors perfect for tasks like filtering or timing.
-
Charging: Apply voltage, and electrons pile up on one plate (negative charge), while the other plate becomes positive. The dielectric keeps them apart, storing energy.
-
Discharging: When the circuit needs it, the capacitor releases its stored energy, stabilizing voltage or powering a device.
-
Behavior in Circuits:
-
DC Circuits: Once charged, capacitors block DC, acting like an open circuit.
-
AC Circuits: They let AC flow, acting like a resistor that depends on frequency.
-
The energy stored follows the formula E = ½CV² (where C is capacitance and V is voltage). Cool, right?
How Capacitor Work in a Circuit
Think of a capacitor as a quick-response battery, ready to step in when the circuit needs a boost.
Here’s the gist:
-
Connect a capacitor to a power source in a circuit.
-
During charging, it builds up charge, creating a voltage difference across the plates.
-
The dielectric determines how much charge it can hold and its voltage limit.
-
When needed, the capacitor releases its energy for things like smoothing signals or powering circuits
Capacitors as Components
Capacitors are like the Swiss Army knives of electronics like versatile and essential. With their ability to handle both high and low frequencies, capacitors are everywhere!
Here’s where they shine:
-
Energy Storage: They store energy for power supplies or backup systems.
-
Signal Filtering: Smooth out noise in audio gear or communication devices.
-
Timing Circuits: Control timing in oscillators or microcontrollers.
-
Power Conditioning: Keep voltage steady in inverters or power electronics.
-
Motor Starters: Give motors (like in fans or AC units) the kick they need to start.
-
Medical Devices: Power defibrillators with controlled energy bursts.
-
Consumer Electronics: Manage power in your phone, TV, or laptop.
Capacitor Symbol and Circuit Diagram
Let’s get visual! Capacitors have a clear symbol in circuit diagrams to show their role:
-
Non-Polarized Capacitor Symbol: Two parallel lines of equal length, representing the plates with a dielectric gap.
Text version: —-||—- -
Polarized Capacitor Symbol: One straight line (positive) and one curved line (negative), often with a “+” sign.
Text version: —-|+||-
Simple Capacitor Circuit
A classic example is a capacitor filter circuit in a power supply:
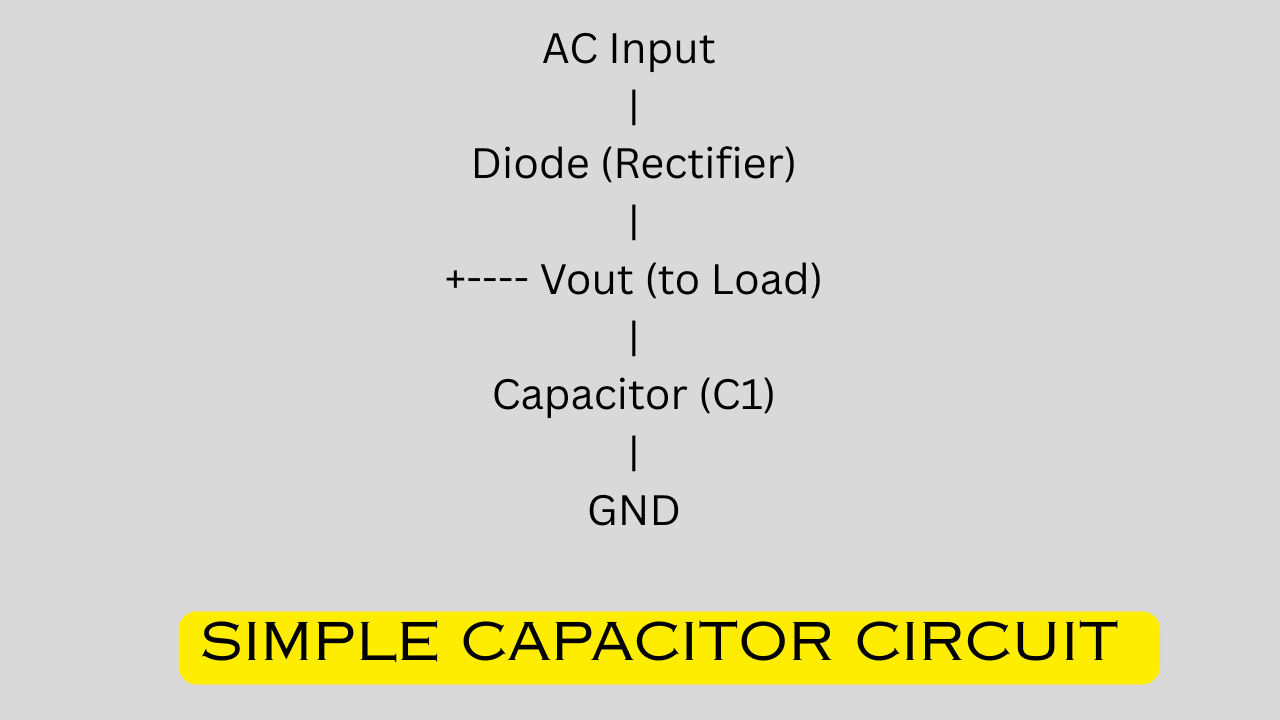
What’s happening here? The AC input gets rectified into pulsating DC by the diode. The capacitor (C1) smooths out the ripples, delivering steady DC to the load. It’s like turning choppy waves into a calm stream!Types of Capacitors and Their Applications
Capacitors come in different flavors, each with unique strengths:
|
Type |
Characteristics |
Applications |
|---|---|---|
|
Ceramic Capacitor |
Non-polarized, small, great for high frequencies |
Signal filtering, decoupling |
|
Electrolytic Capacitor |
Polarized, high capacitance, affordable |
Power supplies, motor starters |
|
Tantalum Capacitor |
Polarized, compact, stable |
Medical devices, smartphones |
|
Film Capacitor |
Non-polarized, high stability |
Audio equipment, power electronics |
More Cool Applications
-
Renewable Energy: Capacitors stabilize voltage in solar inverters and wind turbines.
-
Automotive: They manage battery systems and engine controls in electric vehicles.
-
Telecommunications: Filter signals in 5G base stations and routers.
Why Capacitors Are Awesome
Capacitors are truly awesome for several compelling reasons. They excel at quick energy storage, able to store and release electrical energy in a flash, making them ideal for applications that need rapid response.
Their tiny size is another big win, allowing them to fit seamlessly into compact devices like wearables and smartphones.
Capacitors are also incredibly versatile, performing effectively in both high- and low-frequency circuits, which makes them a go-to component in diverse electronic systems.
On top of that, they’re budget-friendly, offering an affordable solution for mass production without compromising performance. These qualities make capacitors indispensable in the world of electronics!
Capacitor Manufacturing in India
The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, launched by the Indian government, is a game-changer for electronic component manufacturing, including capacitors. With a ₹22,919 crore budget over six years, it aims to boost local production and reduce import reliance.
For capacitors, the scheme offers financial incentives tied to turnover, capital expenditure, and job creation, encouraging companies like Keltron and Vishay India to expand manufacturing.
It targets a 35-40% local value addition, up from 18-20%, by supporting production of passive components like capacitors used in smartphones, EVs, and solar inverters.
India’s capacitor manufacturing is booming, fueled by a thriving electronics industry and policies like Make in India.
Here’s a concise look at the materials, process, key players, and applications.
In terms of material Capacitors use dielectrics like ceramic, aluminum, tantalum, or polymer films, paired with metal electrodes. India sources some materials locally but imports high-quality ones for top performance.
knowing about Manufacturing Process than the process starts by forming the dielectric (e.g., ceramic or aluminum oxide), layering it with metal electrodes, sealing in protective casings (epoxy or metal), and testing for capacitance, voltage, and leakage.
Indian companies manufacturing capacitor like Major manufacturers like Keltron, Vishay India, TDK India, and smaller firms like Deki Electronics produce capacitors for local and global markets, meeting high-quality standards.
Advantages, Limitation, Future of Capacitor
Advantages of Capacitors
Energy Storage: Quickly store and release energy.
Compact Size: Available in small sizes for modern devices.
Versatility: Suitable for both high- and low-frequency applications.
Cost-Effective: Affordable for mass production.
Limitations of Capacitors
Limited Energy Storage: Less capacity compared to batteries
.Polarity Issues: Polarized capacitors can fail if connected incorrectly.
Temperature Sensitivity: Performance varies with temperature changes.
Aging: Electrolytic capacitors degrade over time.
Future of Capacitors
Capacitors are evolving with technological advancements like Supercapacitors which is high-capacity capacitors for energy storage in electric vehicles.
Miniaturization are also smaller capacitors which is use for wearables and IoT devices.
Eco-Friendly Materials which helps for sustainable dielectrics to reduce environmental impact.
Smart Applications integration with AI-driven systems for efficient power management need more capacitor production.
Conclusion
Capacitors are the backbone of modern electronics, handling everything from energy storage to signal filtering. In India, capacitor manufacturing is on the rise, fueled by innovation and demand.
Whether you’re designing a circuit or just curious about electronics, understanding capacitors opens up a world of possibilities.
I hope this guide made capacitors easy to grasp and inspired you to tinker with your next project. Got questions or cool capacitor ideas? Drop a comment below, and let’s keep the electronics conversation buzzing!
I regularly post updates on the latest trends in electronics, new product launches, tech innovations, industry news, and updates from electronic companies.
Follow the blog or bookmark this site to stay ahead in the world of electronics!
Feel free to share this article on your favorite social media platforms!